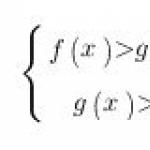Non-developing (another name is frozen, but not frozen in any way) pregnancy, unfortunately, is not the rarest pathology of the first trimester of pregnancy. We can say that one kind of such a pathology is anembryony. This is the case when fertilization occurred, the fetal membranes began to form, but the embryo itself is missing.
Risks of non-developing pregnancy
There are factors that affect pregnancy, its development, and the health of the fetus. A certain category of women has a risk of such a pathological pregnancy. And this possibility can be prevented.
The risks of non-developing pregnancy increase in the case of:
- Age pregnant (this means 35 years and older);
- smoking during pregnancy;
- Obesity in pregnancy;
- Abuse of alcohol and drugs during pregnancy;
- Abuse of caffeine (it is found in coffee, tea, chocolate, energy drinks).

Doctors have determined that two-thirds of cases of missed pregnancies are associated in one way or another with chromosomal abnormalities. Therefore, repeated pregnancies most often develop normally, since serious causes, genetic diseases, etc. are needed for permanent miscarriage.
Reasons: why there is a frozen pregnancy in the early stages
Violated, frozen pregnancy is most often associated with fetal chromosomal abnormalities. During conception, an error can occur, and the embryo will either receive less chromosomes or receive them in excess, while it should receive a certain set. And the reason for this situation is practically undetermined, but it means that the fetus will develop incorrectly, and rejection will occur.
So in the first trimester, a pathological pregnancy can be associated with anomalies in the development of the placenta, the organ without which the fetus cannot grow and develop.
There are a number of main causes of missed pregnancy:
- An infection that has led to such damage to the embryo when it cannot continue to live and develop;
- Chromosomal defects;
- Anatomical pathologies;
- Pathology of the blood coagulation system.
Non-developing pregnancy(intrauterine fetal death, miscarriage) - the death of an embryo or fetus without obvious signs of termination of pregnancy. Unfortunately, this can happen to every woman and at any gestational age, but this does not mean that subsequent pregnancies will be complicated (unless this is a repeated case).
information Pregnancy fading in the early stages of development occurs most often. Critical timing for non-developing pregnancy (NB) is most often up to 8 weeks of gestation. It is at this time that all organs and tissues are being laid, so any pathological factor can disrupt the development of the fetus and lead to its death.
The consequences of NB in the early stages, both for the woman's body and for her psychological state, are less than if this happened during the period when the mother already felt a stir. In any case, you should not dwell on what happened and be afraid of a subsequent pregnancy. Try to treat this as a natural selection of nature.
Causes
Unfortunately, even modern medicine is not always able to answer why the death of a child occurred in utero. There are many reasons, but it is not always possible to get to the truth. Moreover, at an early stage, the law is in effect: “all or nothing”. This means that under the influence of adverse factors, the embryo either transfers them and develops further correctly, or dies.
- genetic factor
Most often, a missed pregnancy at an early stage occurs due to a genetic breakdown of the embryo itself, which occurred at one stage or another of its development. The fetus is simply not viable, so it is rejected. This is a kind of natural selection.
- infectious factor
Another common cause of NB is infection. Most often it is the herpes simplex virus and various respiratory diseases, sexually transmitted infections (chlamydia, mycoplasmas, gonococci) and others. Under the action of these pathogens in the early stages of development, a violation of cell division can occur, damage to the genetic material of the embryo, which will cause its death.
- immune factor
Maternal immunological disease (antiphospholipid syndrome, systemic lupus erythematosus, and others), immunological incompatibility of spouses can also cause fetal death, and more often this occurs before 12 weeks of pregnancy.
- Endocrinological factor
Inadequate synthesis of progesterone (a hormone that maintains pregnancy), thyroid disease, excessive synthesis of male sex hormones and prolactin can interfere with the normal development of the fetus.
- Other factors
We should not forget about the lifestyle of future parents. Bad habits, contact with chemicals, living in an area of high radiation, stress can affect the favorable course of pregnancy, especially in the very early stages.
Symptoms
important The main signs of abortion at different times are pain in the lower abdomen,. The difficulty with NB is that all these symptoms do not bother the woman. She may not know for several weeks that the fetus has died.
The main signs of an early miscarriage are a decrease in subjective sensations that are characteristic of many women in the position:
- engorgement of the mammary glands;
- sensitivity to smells;
- unusual food preferences;
- nausea, vomiting;
- drowsiness.
Of course, not every pregnant woman will be wary of such symptoms, and often these signs disappear with the progression of pregnancy (gestation). That is why fetal fading is often not diagnosed immediately, but after a few weeks. Often, spotting from the genital tract can join, which indicates the beginning of pregnancy rejection.
Ultrasound signs of missed pregnancy
The main ultrasound signs of stopping the development of the embryo at the shortest time are the deformation of the fetal egg, uneven contours, and its location in the lower part of the uterus. It is characterized by a discrepancy between the gestational age according to ultrasound and monthly, the absence of a fetal heartbeat (usually from 5-6 weeks it can already be determined).
additionally However, the gestational age and menstrual period do not always coincide. This can happen for various reasons (irregular periods, hormonal disorders, stress, ovarian cysts, and others), and the difference can be up to four weeks.
Therefore, in some cases (for example, for a monthly gestation period of 7-8 weeks, and an ultrasound scan shows only a fetal egg characteristic of 4 weeks), in order not to make a mistake with the diagnosis, it is worth repeating the study after 5-7 days. If during this time the fetal egg does not grow up, the embryo is not visualized, then the fetus freezes.
Signs of NB during gynecological examination
At a gynecological examination, the doctor evaluates the size of the uterus, its compliance with the expected gestational age, and the condition of the cervix. If the uterus is judged to be smaller, an ultrasound should be performed to confirm or refute the suspicion. Some women have physiological features (initially smaller internal genital organs) or there may be a difference in terms for menstruation and for the embryo, so it is important to make sure that the delay in uterine enlargement is really caused by pregnancy fading.
Determination of human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG)
Determining the concentration of human chorionic gonadotropin helps in making a diagnosis, especially in the very early stages. So, when it is still impossible to see the fetal heartbeat using ultrasound, but there are doubts about its viability, you can donate blood to the level of hCG. It is important to observe the dynamics here, since with a normally developing embryo, the level of the hormone almost doubles every day.
Measurement of basal temperature in case of suspected NB
It should be said right away that this method is only additional and indicative, since it is inaccurate and its results may vary under the influence of many factors. Basal temperature is measured in the rectum, without getting out of bed, at the same time after a night's sleep. Under the influence of the hormone progesterone (preserves pregnancy), this temperature rises by 0.3-0.5 degrees Celsius and is 37.2-37.5. When the embryo freezes, the level of progesterone decreases, and as a result, the basal temperature also decreases.
Treatment
When confirming intrauterine fetal death, a woman must be hospitalized in a gynecological hospital. In the early stages, the main treatment for non-developing pregnancy is the simultaneous removal of the embryo or fetus and its membranes. If the gestational age allows, it is better to do this by vacuum aspiration. This method is more gentle. At a later date, curettage of the uterine cavity is performed (like an abortion). Before the operation, it is worth preparing the cervix, especially in nulliparous women. To do this, use kelp (algae sticks), catheters. This is done to gently and gradually dilate the cervix. Vacuum aspiration of the fetal egg and curettage of the uterine cavity is performed under general anesthesia.
Also, for short periods, expectant management and medical abortion are increasingly used. These methods will allow pregnancy to be terminated more gently (but always under the supervision of doctors).
Rehabilitation
important It is very important to rehabilitate a woman after an undeveloped pregnancy. It includes taking oral contraceptives (at least 3 months), treatment of diseases of the genital organs (infections) and hormonal disorders.
Also, do not forget about the psychological aspect. It's good to change the situation, get positive emotions. Try to avoid conflicts. It is important to feel supported by others.
Consequences
The consequences for the reproductive health of a woman are reduced to zero if the removal of the embryo with its membranes is carefully performed, and rehabilitation is also carried out.
Prognosis for next pregnancy
In 90% of cases, women who have suffered early fetal death are able to become pregnant and bear a healthy child. However, if a non-developing pregnancy recurs, it is necessary to undergo a full examination to identify the cause, since violations can be at the hormonal and immune levels.
Planning a pregnancy is not earlier than 6 months. During this time, the body will be able to recover in order to become capable of bearing a healthy child. It is very important during this period to undergo an examination and preparation for a subsequent pregnancy.
The main thing is to believe in the good and not let your fears prevent you from becoming happy parents.
Waiting for the birth of a baby is one of the happiest periods in the life of future parents. They steadfastly endure all the hardships and hardships of pregnancy, hoping to soon see a miracle - their newborn child. However, some women can suddenly visit a great grief, which is called an undeveloped pregnancy. Most often this trouble happens in the 1st trimester, although it can occur at any time.
An undeveloped or missed pregnancy is a halt in the development of the fetus due to its death, in which there are no signs of miscarriage. Most often, this pathology occurs in the early stages - in the 1st trimester. Another variety of it is a non-developing pregnancy of the type of anembryony. This is a situation in which fertilization has occurred and the fetal membranes have begun to form, but there is no embryo in the fetal egg.
Frozen pregnancy is a very terrible blow to the psychological and emotional state. However, knowing how a woman's body can recover from it is very important to increase the chances of having a healthy baby in the future.
Causes of missed pregnancy
Unfortunately, it is not always possible to establish why a woman has an undeveloped pregnancy. If embryonic death occurs during the 1st trimester, it is usually caused by problems in the unborn child. Approximately 3/4 of miscarriages occur during this period.
If the fetus dies during the 2nd or 3rd trimester, this may be due to the presence of diseases in the mother.
Causes of a missed pregnancy in the 1st trimester
Most often, non-developing pregnancy in the early stages is caused by problems with the chromosomes of the fetus. They are made up of DNA, which contains a detailed set of instructions that control a wide range of factors, from the development of a baby's cells to the color of its eyes.
Sometimes at the time of conception, an error occurs due to which the embryo receives too many or not enough chromosomes. The cause of this phenomenon remains unknown, but its consequences are abnormal development of the fetus and miscarriage.
According to doctors, about 2/3 of cases of early miscarriage are associated with chromosomal abnormalities. It should be remembered that the re-development of an undeveloped pregnancy for this reason is very rare, since most often future parents do not have any problems with chromosomes.
Intrauterine death of the fetus in the 1st trimester can also be caused by problems with the development of the placenta - the organ that connects the mother's blood circulation with the child.
The following factors can increase the risk of an early miscarriage:
- Mother's age is over 35 years.
- Obesity.
- Smoking during pregnancy.
- Drug and alcohol use during pregnancy.
- Consuming large amounts of caffeine, which is found in coffee, tea, chocolate, energy drinks, and some carbonated drinks.
Causes of a missed pregnancy in the 2nd and 3rd trimesters
As a rule, in the 2nd and 3rd trimesters, health problems of the expectant mother can lead to an undeveloped pregnancy.

Causes of non-developing pregnancy in the 2nd and 3rd trimesters:
| Cause type | Diseases |
| Chronic diseases in women | poorly controlled Severe arterial hypertension Systemic lupus erythematosus kidney disease Hyperthyroidism or hypothyroidism |
| Infectious diseases | |
| Food poisoning | Listeriosis - most often develops with the use of unpasteurized dairy products Toxoplasmosis - can develop when eating raw or undercooked infected meat, especially lamb, pork or venison Salmonellosis – most commonly caused by eating raw or undercooked eggs |
| Problems with the uterus | Availability abnormal structure of the uterus |
Myths about the causes of non-developing pregnancy
Despite common stereotypes, miscarriage is not associated with:
- the emotional state of the mother during pregnancy;
- fright;
- physical exercises (however, their type and intensity should be discussed with the doctor);
- work during pregnancy;
- having sex;
- travel by plane;
- eating spicy food.
Symptoms of an undeveloped pregnancy
Unfortunately, in most cases, a woman does not know that her child has already died, since an undeveloped early pregnancy does not have the vivid symptoms that are characteristic of a miscarriage. With this pathology, the placenta does not stop producing hormones, which is why the woman continues to feel pregnant.
However, in some cases, a woman may notice that her symptoms such as breast tenderness, nausea, and fatigue have disappeared. At later stages, the fading of pregnancy is characterized by the absence of fetal movements in the uterus.

Diagnosis of non-developing pregnancy
If you have any concerns and suspicions about the possibility of a missed pregnancy, you should immediately consult a doctor for a complete examination.
The diagnosis of non-developing pregnancy is most often established after an ultrasound scan, which detects the absence of a heartbeat in the fetus. Ultrasound is performed through the anterior abdominal wall or transvaginally. The latter technique is more accurate, but its implementation is accompanied by some discomfort. To exclude errors with a diagnosis, at least two examination procedures are performed.
The doctor can detect the absence of a heartbeat in the fetus later in pregnancy with the help of auscultation with an obstetric stethoscope. Cardiotocography, a technique for recording the fetal heartbeat and uterine tone, will help confirm the fears.
Also, the level of human chorionic gonadotropin and progesterone, hormones associated with pregnancy, can be determined.
In some cases, the diagnosis is not immediately possible. For example, a non-developing pregnancy before a gestational age of 6-7 weeks is difficult to confirm, since only at this time does the fetus develop a heartbeat. In this case, doctors usually recommend a re-examination in 1-2 weeks.
Sometimes fetal death is discovered by chance during a screening ultrasound examination.
After a case of pregnancy fading, a man and a woman need to undergo a complete examination, with the help of which specialists will try to identify possible causes of fetal death. Unfortunately, in half of the cases, the etiology of a non-developing pregnancy cannot be detected.
In case of repeated cases of miscarriage, women and men undergo an even more detailed examination, including:
- Karyotyping is a test to detect abnormalities in chromosomes that can cause fetal death during fetal development. If problems are found, partners are referred to a geneticist who explains to the couple their chances of a successful pregnancy in the future and talks about possible solutions, such as in vitro fertilization.
- Ultrasonography. To study the structure of the uterus and identify its pathology, a transvaginal ultrasound examination is performed.
- Blood tests that measure levels of antiphospholipid antibodies and lupus anticoagulant. Antiphospholipid antibodies increase the risk of blood clots and affect the formation of the placenta, which can impair the blood supply to the fetus, causing its death.
Treatment of non-developing pregnancy
After the diagnosis is established, a woman often faces a difficult choice of which tactics to treat a non-developing pregnancy to choose. In any case, a long stay in the uterine cavity of a deceased fetus is dangerous for the health and life of a woman, since this increases the risk of developing severe bleeding and infectious complications.
As a rule, a woman is offered one of the options:
- Expectant tactics. In the early stages of pregnancy, with intrauterine death of the embryo, it is possible to expect a natural rejection of its tissues by the woman's body. At this time, careful monitoring and observation is carried out. However, you can't wait too long - it's dangerous. As a rule, active treatment can be delayed only up to 2 weeks from the diagnosis. Doctors are not too fond of expectant management during a missed pregnancy.
- Surgical tactics. After establishing and clarifying the diagnosis, a small obstetric operation is performed - dilation of the cervix and curettage (curettage of the uterine cavity). During this surgical intervention, the tissues of the fetus, its membranes and the placenta are removed from the uterine cavity. The operation is usually performed under general anesthesia.
- medical tactics. Termination of an undeveloped pregnancy in the early stages (up to 8 weeks of gestation) can also be carried out by a conservative method. For this purpose, drugs are used that cause the uterus to contract and push the fetal tissues and placenta out of its cavity.
With intrauterine death of the fetus in the 3rd trimester, delivery is necessary. To this end, doctors either induce labor through the birth canal or perform a caesarean section.
It should be remembered that a non-developing pregnancy is a severe emotional blow. Therefore, a pregnant woman needs the support of both medical personnel and people close to her very much.
Complications and consequences of missed pregnancy
A serious danger to the health and life of a woman with an undeveloped pregnancy is the risk of developing severe bleeding and infections.
Most often, an undeveloped pregnancy has severe emotional consequences not only for a woman, but also for her partner, as well as for people close to them. During this time, they may need psychological support.

Those who have experienced this grief may develop fatigue, worsen appetite and sleep disturbances, and experience feelings of guilt, shock, sadness, and anger. People deal with loss in different ways. Some of them find comfort in telling others about their feelings, while others do not want to communicate about their grief. Some women start planning their next pregnancy in just a few weeks, while others cannot even think about it.
The father of the child may also suffer the loss. It is more difficult for men to express their emotions, especially when they know that they must support their partner with their actions. A miscarriage can sometimes cause relationship problems.
The concern of many women who have suffered this grief is the question of whether pregnancy can occur again after suffering a non-developing pregnancy. Fortunately, in most cases, a healthy child is born to them after a certain time, since most often chromosomal abnormalities develop in the fetus itself, and are not inherited from their parents. As a rule, doctors advise planning the next pregnancy 3-6 months after the interruption of the previous one.
Prevention of antenatal fetal death
In most cases, the cause of a non-developing pregnancy remains unknown, so it is not possible to prevent this pathology.
However, compliance with certain conditions will help reduce the risk of missed pregnancy:
- quitting smoking, alcohol, drugs;
- eating a healthy, balanced diet rich in fruits and vegetables;
- trying to avoid contracting certain infectious diseases during pregnancy (for example, rubella);
- avoiding certain foods that can harm a pregnant woman and her baby;
- normalization of weight before pregnancy;
- taking prenatal vitamins and folic acid supplements before pregnancy may also reduce the risk of antenatal fetal death and birth defects.
If the causes of non-developing pregnancy are identified, they are treated to prevent such cases in the future.
Useful video about non-developing pregnancy
I like!
A frozen or non-developing pregnancy is a cessation of the development of the fetus and its death. Most often, a pregnant woman faces a similar problem in the first trimester of pregnancy (up to 14 weeks). Much less often, a frozen pregnancy occurs at a later date.
An undeveloped pregnancy is a type of miscarriage, just like a miscarriage.
How does pregnancy freeze?
Initially, as in a normal pregnancy, the embryo is implanted in the uterus. But for some reason, the development of the fetus stops and the fetus dies. But despite this, abortion does not occur, as with a normal miscarriage, that is, the fetal egg does not exfoliate and does not leave the uterus. Therefore, the uterus continues to grow, the woman still feels "pregnant" and the level of hCG (human chorionic gonadropin) - the pregnancy hormone - does not grow, but slowly decreases. But sooner or later, placental abruption and ovum abruption occur, and only then do symptoms of a missed pregnancy appear.
What can cause an undeveloped pregnancy?
Firstly, due to a hormonal imbalance, or rather, due to a lack of progesterone or due to an excess of androgens, in particular, testosterone.
The second possible cause of a missed pregnancy is genetic abnormalities of the fetus that are incompatible with life. According to most researchers, nature thus conducts natural selection, timely eliminating the unviable fetus.
The third most common cause is infections. During pregnancy, immunity weakens, which serves as a favorable background for exacerbation of infectious diseases. The most dangerous are sexual infections (gonorrhea, chlamydia, ureaplasmosis and mycoplasmosis) and TORCH infections (toxoplasmosis, rubella, herpes, cytomegalovirus infection).
Increasingly, the cause of non-developing pregnancy and miscarriage is the presence of APS in a pregnant woman.
Other provoking factors include pregnancy after in vitro fertilization;
stress and a sharp change in climate - flights over long distances;
smoking and drinking alcohol,
the age of the pregnant woman is over 35 years.
Symptoms of a missed pregnancy
The symptoms of a missed pregnancy are almost the same as the symptoms of a miscarriage. With detachment of the ovum, cramping pains in the lower abdomen, blood discharge from the genital tract appear.
A woman can pay attention to the disappearance of pregnancy symptoms: toxicosis (if, of course, it was), soreness of the mammary glands, and so on.
If a missed pregnancy occurred at a later date, then one of the formidable signals about the occurrence of a pathology will be the absence of fetal movement.
However, even if these symptoms are present, it is quite difficult to say for sure whether there is a frozen pregnancy or not, therefore, with any of the described symptoms, a gynecologist's consultation is necessary. In the presence of blood discharge and the absence of fetal movement, a doctor's consultation is necessary on an emergency basis.
Diagnosis of missed pregnancy
The examination includes an examination by a gynecologist, ultrasound of the pelvic organs and a blood test for hCG in dynamics. Based on these studies, it is possible to reliably diagnose a miscarriage.
When viewed on a chair in all pregnant women with a non-developing pregnancy, a discrepancy between the size of the uterus and the gestational age is revealed, that is, the uterus is smaller than it should be.
According to ultrasound, the size of the embryo is less than the prescribed gestational age. He has no heartbeat. Ultrasound can also detect anembryony - a type of non-developing pregnancy, when the fetal egg is empty, without an embryo.
The hCG level, as already mentioned, does not increase during a missed pregnancy and lags significantly behind the hCG level during a normal pregnancy. In order to better assess the dynamics of hCG fluctuations in the blood, it is advisable to take the test twice with an interval of 48 hours.
Termination of a frozen pregnancy
In most cases, they start with expectant tactics. That is, after the fetus dies, the hCG level drops, the uterus contracts and a spontaneous miscarriage occurs, i.e. the fetal egg leaves the uterus on its own.
The second method is the termination of pregnancy with medications. This method is used if the gestational age is less than 8 weeks. For medical termination, progesterone antagonists (Mifepristone or Mifegin) with prostaglandin E2 analogues (Misoprostol, Cytotec) are used. A few hours later, under the influence of drugs, contractions occur and a spontaneous miscarriage occurs.
Surgical treatment is also used, which is a curettage of the uterine cavity with the removal of the fetal egg. The resulting scraping is sent for histological and cytogenetic examination of the tissues of the fetal egg. After curettage, a hormone that contracts the uterus (Oxytocin) is administered intravenously and antibiotics are prescribed to prevent infectious complications.
A week or two after curettage, a control ultrasound of the pelvic organs is done to see if there are any remnants of the fetal egg in the uterus.
All women who have been diagnosed with a non-developing pregnancy, after treatment, that is, after a miscarriage or curettage, are recommended to be examined by a gynecologist to determine the cause of the missed pregnancy, otherwise the subsequent pregnancy may also turn out to be non-developing.
The complex of examination after a frozen pregnancy includes:
Cytogenetic and histological examination of fetal tissues, which is carried out after curettage, and with this result a woman should contact her gynecologist;
- PCR diagnostics for urogenital infections;
- smear on flora;
- blood test for TORCH infection;
- a blood test for hormones that affect conception and pregnancy (LH, FSH, prolactin, estradiol, progesterone; androgens-testosterone and DHEA; 17-hydroxyprogesterone, cortisol. If necessary, thyroid hormones are examined (TSH, T4, T3);
- Ultrasound of the pelvic organs;
- blood coagulogram;
- a blood test for antibodies to phospholipids and human chorionic gonadotropin.
Based on the results obtained, the doctor prescribes treatment. After a non-developing pregnancy, it is recommended to protect yourself from pregnancy for 3-6 months for examination, treatment and recovery of the body. As a rule, oral contraceptives are prescribed for protection (Zhanin, Jess, Yarina, etc.).
In most cases, an undeveloped pregnancy is not a sentence, and after that a woman can safely become pregnant and give birth.
Complications of missed pregnancy
Possible complications of non-developing pregnancy are associated with the prolonged presence of the deceased fetus in the uterine cavity. This can lead to chorionamnionitis, that is, to infection of the membranes and to endometritis, an inflammation of the uterine mucosa. If a missed pregnancy occurs at a later date, there is a risk of developing fetal maceration, that is, decomposition of the deceased fetus, which can lead to serious complications, such as peritonitis or sepsis.
Prevention of missed pregnancy:
A healthy lifestyle, giving up bad habits, regular exercise;
- examination by a gynecologist before pregnancy planning and timely treatment of all infections and hormonal disorders;
- taking folic acid and vitamin E during pregnancy planning and in the first trimester up to 12-14 weeks of pregnancy.
Questions and answers.
1. When will menstruation begin after curettage for a missed pregnancy?
In 25-60 days after curettage, menstruation should come.
2. I had a scraping a month ago. The gynecologist prescribed oral contraceptives for 6 months, but I don’t want to drink them. What do you advise?
Oral contraceptives have a therapeutic effect, so they are most often prescribed. You can temporarily use barrier contraception, but in any case, your doctor decides on the basis of tests.
3. How many days after scraping can there be bloody discharge?
Up to 10-14 days.
4. What are my chances of carrying a normal pregnancy if there was a miscarriage before?
The same as in healthy women, if the missed pregnancy was only once.
5. I take oral contraceptives. Can I have my hormones tested?
It is forbidden. It doesn't make any sense.
6. At what stage of pregnancy can the fetal heartbeat be accurately seen on ultrasound?
At 6 weeks pregnant.
7. Can an undeveloped pregnancy develop if ultrasound is done frequently?
No, he can not.
8. What ultrasound is better to do in a short time, if there is a suspicion of a missed pregnancy?
In the early stages, ultrasound with a vaginal probe is more informative.
9.My hCG corresponds to the term, and according to the ultrasound they say that the pregnancy is not developing. Who to believe?
What is the gestational age. Before 6 weeks of pregnancy, the heartbeat is not always visible on ultrasound. But it happens that the pregnancy “freezes”, which is clearly visible on the ultrasound after 6 weeks, and hCG has not yet had time to decrease.
Obstetrician-gynecologist, Ph.D. Christina Frambos
Causes, signs, treatment of non-developing pregnancy
A non-developing pregnancy is a pathology in which, for some reason, the embryo (or fetus) stops developing and dies.
There are many reasons for this pathology. In the first trimester, these are serious chromosomal "breakdowns". At any time - infections, lack of progesterone and an excess of androgens, Antiphospholipid syndrome - when a child dies due to blood clots forming in the vessels. In addition, the causes of non-developing pregnancy may lie in various toxic effects on the fetus. Radiation, the use of drugs prohibited for expectant mothers, smoking, drinking alcohol can cause pregnancy loss or severe malformations in the fetus.
How to recognize a frozen pregnancy
1. Stopping the growth of hCG or reducing it. HCG is the hormone that is formed due to the chorion. And according to the dynamics of the increase in hCG, various important conclusions can be drawn. However, not all women usually control the growth of hCG, since there is no practical need for this. Only in cases where the risk of spontaneous abortion is high. For example, when conceiving with the help of IVF or with habitual miscarriage. The level of hCG is determined by a blood test. But a pregnancy test will help draw some conclusions. Signs of a missed pregnancy may show up on a negative pregnancy test (due to low hCG levels). However, this symptom is more often expressed in the very early stages of pregnancy.
2. Lack of growth of the uterus. This symptom can be noticed by a doctor during a gynecological examination, when a discrepancy between the size of the uterus and the gestational age is revealed. Or when measuring the length of the uterus on the couch with a centimeter tape - usually such measurements are performed from the second trimester of each pregnant woman during a scheduled visit to the gynecologist. Frozen pregnancy may be suspected with a low location of the bottom of the uterus.
3. Abrupt disappearance of signs of toxicosis. Usually they disappear gradually, by the second trimester of pregnancy. In the event of the death of the embryo, nausea disappears almost instantly. The mammary glands can be soft, painless, which is not typical for pregnancy.
4. Bloody, spotting discharge from the genital tract, pain in the lower abdomen. Usually, these symptoms occur already when the miscarriage has begun. However, it is not at all a fact that with these signs the child is already dead.
5. Decrease in basal temperature. Some expectant mothers measure the temperature in the rectum before and during pregnancy. This method, which is not very accurate, can help determine ovulation, pregnancy, and monitor its development. During pregnancy, the basal temperature is usually above 37 degrees. But its decrease cannot be considered as an absolute sign of a frozen one.
6. Absence of a heartbeat in a fetus on ultrasound or an embryo in a fetal egg. If the baby does not have a heartbeat at 5-6 weeks of gestation, this may indicate the death of the embryo.
There are cases when an embryo is not found in the fetal egg, that is, it dies at a very early date, when it is not yet visible by ultrasound. This pathology is called anembryony.
7. Absence of fetal movements. Primiparas feel fetal movements daily from 20 weeks of pregnancy, multiparous - from the 18th week. In the absence or cessation of movement, the woman is urgently sent for an ultrasound scan.
Whether to terminate the pregnancy and how
Non-developing pregnancy, what to do - abortion or wait for a spontaneous miscarriage? Doctors abroad have a waiting tactic. A woman weekly, in some cases even more often, performs an ultrasound scan and visits a gynecologist in order to recognize the onset of the inflammatory process in time - the basis for surgical intervention. We usually immediately recommend an abortion if there are no signs of an incipient spontaneous miscarriage.
As a rule, doctors “treat” a non-developing pregnancy in the early stages with vacuum aspiration, that is, they suck out the contents from the uterus using a special cannula. This intervention can be performed under local anesthesia, without general anesthesia. Another option is to induce a miscarriage with medication. A woman takes drugs that a doctor gives out, and after 1-3 days she has a spontaneous miscarriage. This procedure is effective in the early stages. The longer the term, the more likely it is that the miscarriage will be incomplete and vacuum aspiration will have to be done.
If a non-developing pregnancy is proved by examination, curettage is recommended if the fetus is already quite large and will not pass through the cannula (vacuum aspiration is not possible). Curettage (popularly "cleansing") is always performed in a hospital setting. The length of stay in the hospital after the procedure is up to several hours, if there are no complications.
What to do after a frozen pregnancy
In the absence of contraindications, a woman is recommended to take oral contraceptives for at least 3-6 months. It is believed that they help restore hormonal levels and reliably protect against pregnancy. If there are contraindications to taking pills, barrier contraception (condom) is recommended. A child should be planned after undergoing treatment (if necessary), but not earlier than 3 months after a frozen one, otherwise there is a high risk of a recurrence of the situation.
As for the medical examination, doctors consider it mandatory only if an undeveloped pregnancy is repeated more than 2 times (if the embryo stops developing in the first trimester of pregnancy). Since in this case, most often, random chromosomal abnormalities are to blame, which are almost impossible to avoid. It should be noted that chromosomal abnormalities become more frequent the older the woman.
If the situation repeats. It is necessary to undergo an examination to identify and eliminate the cause of pregnancy fading. A woman should take blood tests, smears for various infections and viral diseases, undergo an ultrasound of the pelvic organs, take tests for certain hormones, take a blood coagulogram and an analysis for antibodies to phospholipids, go for a consultation with an endocrinologist.
When planning a pregnancy, she is prescribed an increased dosage of folic acid and potassium iodide.