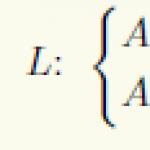For kidney disease, pick up medications possible only in conjunction with a doctor. Based on the test results, symptoms and complaints of the patient, the urologist makes a diagnosis. And only after that, you can purchase a medicine that helps with inflammation of the kidneys or urolithiasis that struck the renal system.
How to treat renal colic?
Why does kidney pain appear? Unpleasant sensations can be provoked by inflammation, urinary retention. But the most common reason pain - movement of a stone along the renal ducts (renal colic). The calculus, moving forward, injures the mucous membrane, causing inflammation, impaired fluid secretion and irritation of pain receptors.
Pain relief medications are divided into three large groups:
Antispasmodics
 These drugs help relieve smooth muscle spasms and make it easier for calculus or sand to pass through the ducts. Antispasmodics are also necessary if, due to spasm, the ducts are blocked and urine does not come out, stagnates in the kidneys or bladder. Acute urinary retention can lead to extensive inflammation and poisoning of the body.
These drugs help relieve smooth muscle spasms and make it easier for calculus or sand to pass through the ducts. Antispasmodics are also necessary if, due to spasm, the ducts are blocked and urine does not come out, stagnates in the kidneys or bladder. Acute urinary retention can lead to extensive inflammation and poisoning of the body.
To restore the patency of the ducts, medications should be taken:
- Drotaverinum.
- No-shpa.
- Papaverine.
These are narrowly targeted drugs that have a relaxing effect. Sometimes the spasm goes away, but the pain remains. To achieve the maximum analgesic effect, the urologist may recommend that the patient take an antispasmodic together with an analgesic, or simply drink a combination drug.
Analgesics
 The action of these drugs is aimed at the production of prostaglandins - cells that provoke painful sensations. "Pure" analgesics:
The action of these drugs is aimed at the production of prostaglandins - cells that provoke painful sensations. "Pure" analgesics:
- Paracetamol.
- Panadol.
Combined preparations containing both an analgesic and an antispasmodic:
- Spazmalgon.
- Aspazmik.
- Revalgin.
- Tempalgin.
- I took it.
- Baralgin.
With renal colic, it is better to take a combined drug, since an antispasmodic will help remove the cause of pain - a spasm, and an analgesic will extinguish the response of pain receptors.
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs
The doctor, when offering a drug for kidney pain to a patient, may recommend a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug for renal colic, pyelonephritis, or urinary tract infection. Non-steroidal (non-hormonal) drugs reduce inflammation as effectively as glucocorticosteroids, but they do not accumulate in the body and do not provoke an immune response.
 For kidney pain, you should take:
For kidney pain, you should take:
- Aspirin.
- Ibufen.
- Diclofenac.
- Naproxen.
- Ketoprofen.
These medications also have antipyretic effects, which come in handy when fever is caused by inflammation. Some patients prefer to apply NSAIDs topically, in the form of ointments or gels. In case of renal pain, this will not give the necessary analgesic effect, since ointments have weak penetrating abilities, the drug will not reach the kidneys.
Only with severe pain (provoked by a cancerous tumor, movement of especially large stones), the patient can be prescribed Fentanyl, Codeine. These are analgesics belonging to the group of narcotic drugs that can be addictive.
Elimination of the inflammatory process in the kidneys
What is kidney inflammation? This general term refers to several diseases in which there is pain in the kidneys, inflammation of the mucous membrane, impaired production and output of urine. Such diseases cannot be cured with one medicine, therefore the urologist prescribes several drugs at once, the action of which is aimed at reducing painful sensations, eliminating edema, and extinguishing bacterial infection.
Antibiotics
The choice of an antibacterial drug depends on the severity of the inflammatory process in the genitourinary system. In addition, before prescribing the drug, the type of pathogen that has affected the kidneys is determined by laboratory. Antibiotics are selected that can quickly and effectively remove the pathogenic bacterium and prevent its spread.
 For mild, primary infections, appoint antibacterial drugs penicillin group:
For mild, primary infections, appoint antibacterial drugs penicillin group:
- Amoxicillin.
- Flemoxin.
- Penicillin.
- Macrolide.
Most often, drugs are prescribed in tablets. There is a low effectiveness of these antibiotics for pyelonephritis, therefore the patient is recommended more strong drugs, new generation. Urologists often recommend taking cephalosporin antibacterial drugs:
- Cephalexin.
- Cefatoxime.
- Cephalothin.
- Zeenat.
- Claforan.
These drugs are low-toxic, consist of natural and semi-synthetic substances. They have a broad spectrum bacteriostatic effect, they can be used for immunodeficiency. Patients may experience side effects: arrhythmia, nausea, rash.
 Complex purulent infections require treatment with amine glycosides.
Complex purulent infections require treatment with amine glycosides.
- Amikacin.
- Sisomycin.
- Netilmicin.
- Gentamicin.
These drugs are prescribed for secondary infections, repeated treatment. You cannot take aminoglycosides on your own, an overdose of this type of drug can lead to renal failure.
 In case of acute inflammation of the kidneys, the urologist may recommend taking drugs of the fluoroquinol group:
In case of acute inflammation of the kidneys, the urologist may recommend taking drugs of the fluoroquinol group:
- Ofloxacin.
- Pefloxacin.
- Sparfloxacin.
- Ciprofloxacin.
Preference should be given to the newest medicines of the new generation. They have fewer side effects and are quick to heal.
Uroseptics
 If infectious processes have engulfed the kidneys and urinary tract, another type of drugs indicated for admission is uroseptics. They have not only bacteriostatic effect, but also antiseptic.
If infectious processes have engulfed the kidneys and urinary tract, another type of drugs indicated for admission is uroseptics. They have not only bacteriostatic effect, but also antiseptic.
Also, uroseptic can become a cure for sand in the kidneys, since it not only helps to reduce the negative manifestations of pathogenic bacteria, but also can reduce swelling, inflammation, and speed up the cleansing of the urinary tract. Most often, patients are offered to take nitrofurans (Furadonin, Furagin). These are the simplest medicines produced for a very long period of time. They can be used for both prophylaxis and treatment.
Nitroxalin is more effective. It is suitable for patients suffering from kidney inflammation complicated by prostate adenoma or genital infections. It can be used after surgery on the genitourinary system, to prevent the development of infection after insertion of a catheter or bougienage of the urethra.
A new generation drug - Nolitsin. It is used to treat acute and chronic kidney infections, simple and complex diseases of the genitourinary system, accompanied by inflammation of the renal ducts. It is also used to prevent sepsis after removal of kidney stones or elimination of cystic formations.
Preparations for the restoration of kidney functionality
To improve the functioning of the kidneys after illnesses, patients need to take special medications that have a beneficial effect on the restoration of the mucous membrane, urine production, and the elimination of toxins. Urologists recommend comprehensive rehabilitation treatment:

For cancers of the renal system, cytostatics (Cyclophosphamide, Azathioprine) are necessarily prescribed. Their action is aimed at extinguishing the body's immune response, restoring normal leukocytosis.
Means for dissolving calculi
The most common problem in patients suffering from kidney pain is the appearance of stones in the kidney ducts. If the stones are small and can be treated with medication, a urologist may advise a medicine to dissolve kidney stones. It is necessary to select a drug depending on what type of stones are found, taking into account their size and localization.

The urologist can prescribe Panangin to the patient. Despite the fact that this drug is believed to be used to improve the functioning of the cardiovascular system, its use in urology is also acceptable. Panangin effectively removes urate and oxalate stones.
The main condition for taking medications to dissolve calculi is that they must be taken for a long period of time - at least three months. At the same time, regularly visit a doctor and monitor the state of the genitourinary system.
How can you "expel" kidney stones?
It is possible to expel kidney stones only under the supervision of a doctor. Sometimes diuretics work so effectively that the calculus quickly begins to move. At the same time, he scratches the mucous membrane and can block the ducts. Only on the recommendation of a doctor can you drink diuretics.

You should not "prescribe" yourself a medicine for kidney stones or try to eliminate inflammation with hot baths. If the patient takes drugs haphazardly, suppresses pain with pills, kidney disease can cause complications, one of the most severe is renal failure. Want to get rid of kidney disease? Go to the doctor and only after visiting the urologist go to the pharmacy for medicines.
Urolithiasis (Urolithiasis) is a metabolic disorder that leads to the formation of stones (calculi) in the urinary tract (urolithiasis) and kidneys (nephrolithiasis). The use of the terms "urolithiasis" and "nephrolithiasis" as synonyms is not entirely correct.
The diagnosis of ICD is made at different ages. However, in most patients, this disease occurs during the period of working capacity (30-50 years).
A little more often, the area of localization of calculi is the right kidney, and bilateral kidney damage occurs in every fifth case of urolithiasis.
Exogenous and endogenous factors are the main causes of KSD:
Endogenous
Violations of the properties of urine (disruptions in the metabolism of oxalic acid, purine metabolism). Birth defects and injuries of the urinary tract. Bacterial infections. Pathologies of the genitourinary system, leading to impaired urination (pyelonephritis, nephroptosis, hydronephrosis, cystitis and others). Inherited genetic diseases(cystinuria). Taking medications containing calcium, sulfonamides. Lack of vitamins A and B6 in the body, an excess of D, C. Sedentary lifestyle and the quality of food consumed.
Methods of treatment of ICD are conservative, instrumental, operational. They are prescribed depending on:
etiology; metabolic disorders; states of urodynamics; urine pH; kidney function; places of localization of the stone; the chemical composition of the calculus and its size; associated complications.
The diagnosis and the appointment of treatment are made according to the results of the following examinations: general analysis urine, ultrasound, X-ray of the pelvic organs, intravenous urography, cystoscopy.
In order to choose the right treatment, it is necessary to determine what constituents the stones are made of.
Several types are distinguished by chemical composition. Approximately 60-80% of all calculi are inorganic calcium compounds: veddellite, wevellite (calcium oxalate), vitlockite, apatite, brushite, hydroxyapatite (calcium phosphate). Concrements formed from uric acid and its salts (uric acid dihydrate, ammonium and sodium urates) are found in 7-15% of patients. Stones containing magnesium (newberite, struvite) account for about 7-10% of all calculi and often accompany infection. Cystine stones are quite rare (1-3%). Concrements that completely occupy the renal pelvis are called coral-shaped.
The mixed composition of stones, detected in most cases, indicates a simultaneous violation in several metabolic links and concomitant infection. It has been proven that the climatic and geographical factor, living conditions, the content of various salts in drinking water and food products affect chemical composition calculi.
Medicines used for nephrolithiasis and urolithiasis
Treatment of KSD is based on the use of pharmacological drugs. When they are taken, the risk of recurrent stone formation is reduced due to the correction of biochemical parameters in urine and blood.
In addition, they facilitate the process of passing small stones (up to 5mm).
By the method of litholysis, as a rule, urates are affected. Considering that such calculi are formed at a reduced pH of urine, it is necessary to maintain the pH balance at the level of increased indicators (6.2-6.8) - to alkalinize urine. This effect is achieved with the drugs blemaren, uralit U, soluran, margulite and others.
Blemarine is available in the form of effervescent tablets or granular powder, and comes with a control calendar and indicator paper. It contains citric acid salts - potassium or sodium citrate, which together create an increased concentration of potassium and sodium ions in the urine. However, we must not forget that against the background of the use of citrate mixtures, phosphate and oxalate stones can form (at a urine pH of more than 7). This is because citric acid increases the concentration of oxalic acid in the urine.
The use of litholysis for stones with a different chemical structure is of an auxiliary nature. Medicines based on citrates help dissolve not only urates, but also small calcifications, mixed stones. In addition, they help to inhibit the process of stone formation. However, the alkalization method must be carried out in the absence of other diseases of the genitourinary system.
Back to the table of contents
Spasmodic analgesics
 Antispasmodic drugs relieve pain during bouts of renal colic. They facilitate the exit of small stones, reduce tissue swelling during long-term presence of the stone in the organs. As a rule, colic is accompanied by severe pain and fever, so it makes sense in some cases to combine the use of antispasmodics with anti-inflammatory nonsteroidal drugs.
Antispasmodic drugs relieve pain during bouts of renal colic. They facilitate the exit of small stones, reduce tissue swelling during long-term presence of the stone in the organs. As a rule, colic is accompanied by severe pain and fever, so it makes sense in some cases to combine the use of antispasmodics with anti-inflammatory nonsteroidal drugs.
According to the mechanism of action, antispasmodic drugs are divided into neurotropic and myotropic.
The antispasmodic effect of neurotropic drugs is aimed at blocking the transmission of nerve impulses to the nerve endings that stimulate smooth muscle tissue... Myotropic antispasmodics reduce muscle tone.
Neurotropic drugs - M-anticholinergics (atropine, metacin, scopolamine) are not often used for MKD, since they have pronounced side effects and low antispasmodic activity.
The myotropic antispasmodic drotaverin is widely used in Russia. It selectively blocks PDE IV (phosphodiesterase), which is contained smooth muscles ah urinary tract. This achieves an increased concentration of cAMP (adenosine monophosphate), due to which muscle relaxation occurs, edema and inflammation caused by PDE IV decreases.
A-blockers (tamsulosin, alfuzosin and others) can act as stimulants for the independent passage of stones.
Tamsulosin helps to reduce tone and improve detrusor function. This medicine is taken once a day, 400 mg. Severe liver disease and orthostatic hypotension are contraindications to the use of this drug.
In the presence of stones in the ureters and accompanying this process of renal colic, analgesics-antispasmodics are prescribed, such as Maksigan, Spazmalgon, Trigan, Baralgin. To relieve pain, it is recommended to use baralgin orally or intramuscularly in combination with Avisan or no-shpa (drotaverin), 1 tablet each. If their action is ineffective, intramuscular administration of diclofenac (dicloran, voltaren and the like) is performed. Also, in these cases, there is a reason to prescribe nonspecific anti-inflammatory drugs (indomethacin, piroxicam) and to carry out therapy with hepaprotectors with antioxidant activity (Essentiale, Lipostabil, phospholip and others). Often, with urolithiasis, lytic mixtures containing promedol or analgesics such as pentazocine, tramadol, butorphanol are indicated for use.
Back to the table of contents
Antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory drugs
Antibiotics are prescribed for patients with struvite stones because calculi from mixed magnesium and ammonium salts form due to infection caused by microorganisms. Most often, the urinary tract is infected with Escherichia coli, less often - with staphylococci and enterococci.
Antibiotic treatment is recognized as effective at the initial stage of therapy. Observing the clinical picture of the disease, the administration of drugs is carried out by the oral or intravenous route. The antibiotic has the ability to penetrate the site of inflammation and accumulate in it in the required concentrations.
The simultaneous appointment of bacteriostatic and bactericidal antibiotics is unacceptable. In order to prevent the occurrence of bacterio-toxic shock, antibacterial drugs should not be taken in case of violations of the outflow of urine. The duration of antibiotic treatment should be at least one to two weeks.
For urinary tract infections with bacteria, the most common use of the following types of drugs:
Fluoroquinolones (ofloxacin, ciprofloxacin, lomefloxacin, pefloxacin, gatifloxacin, levofloxacin). Cephalosporins III (ceftriaxone, ceftazidime) and IV generation (cefepime). Aminoglycosides (amikacin, gentamicin). Carbapenems (meropenem, imylene / cilastatin).
Fluoroquinolones are used for infections arising from lesions by aerobic bacteria - staphylococci, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Shigella.
Cephalosporins have a high degree of bactericidal action, have a wide field of action. Drugs last generations active against gram-positive and gram-negative microorganisms, including strains resistant to aminoglycosides.
All antibiotics-aminoglycosides in small doses cause bacteriostasis (stop protein synthesis), in large doses they cause a bactericidal effect.
Carbapenems are equally active against aerobic and anaerobic bacteria. During treatment with these drugs, the synthesis of peptidoglycan is inhibited, and lysis of bacteria occurs. However, with long-term treatment, there is a risk of pseudomembranous enterocolitis.
Anti-inflammatory nonsteroidal drugs (NSAIDs) are prescribed in combination with antibiotics when an infection is detected in order to destroy the focus of inflammation. These drugs include ketoprofen, ketorolac, diclofenac and others. However, these drugs are ulcerogenic, so they need to be taken with great care.
If the inflammation process is insignificant, agents of the nitrofuran series (furadonin, furangin, furazolidone), pipemidic acid (pimidel, palin), oxolinic acid (dioxacin, gramurin), norfloxacin (norflox, nolicin), sulfonamide (etazol, others) are prescribed.
Medicines that correct biochemical changes in the blood and urine
Allopurinol is a drug that reduces the formation of uric acid in both waste products and blood serum, thereby preventing its accumulation in tissues and kidneys. Allopurinol is prescribed to patients with relapses of urolithiasis with calcium oxolate calculi. This drug is prescribed immediately when biochemical changes are detected.
The means that correct the biochemical composition of urine include thiazide diuretics (indapamide, hypothiazide).
Also, with ICD, it is important to take drugs that promote microcirculation in tissues (trental, pentylin, pentoxifylline, pentylin, relofect and others), as well as taking calcium anatagonists (verapamil). These medicines are prescribed in conjunction with antibiotics.
However, if the stone disrupts urodynamics, complete elimination of the infection with urolithiasis does not occur. As a rule, antibacterial therapy is prescribed before and after surgery.
Back to the table of contents
Preparations containing herbal ingredients
 In the presence of stones in the body, which, according to doctors' forecasts, will be able to move away on their own, drugs containing terpenes are prescribed. They improve blood circulation in the kidneys, increase urine output.
In the presence of stones in the body, which, according to doctors' forecasts, will be able to move away on their own, drugs containing terpenes are prescribed. They improve blood circulation in the kidneys, increase urine output.
In addition, by enhancing peristalsis, they contribute to the discharge of stones. This group of drugs includes cystenal, enatin, phytolysin, avisan, artemizol. Most of these drugs are contraindicated in patients with peptic ulcer disease, impaired renal function, chronic and acute glomeronephritis.
Cistenal, a preparation containing tincture of madder root, various essential oils, magnesium salicylate. It comes in the form of an alcoholic tincture. To block an attack of colic, it is recommended to take 20 drops of a sugar-based medicine.
Artemizol alcohol tincture contains essential oils of wormwood and peppermint leaves, peach oil. Its pharmacological action is similar to that of cystenal. You need to apply a few drops (depending on the clinical picture) under the tongue on a lump of sugar. The course of treatment is 10-20 days.
Olimetrin and enatin are similar in composition: peppermint, terpene oils, calamus, olive, refined sulfur. They are taken 1 tablet up to 5 times a day.
Cyston, consisting of extracts of many plants (saxifrage reed, bicarp, stalky, filmy onosomes, bracts, madder, vernonia ashy, rough straw), powder of mummy and lime silicate, helps to reduce spontaneous crystallurgy, stabilizes balance crystal-colloid. Thanks to its active substances, the concentration of elements contributing to stone formation decreases, it turns out to be diuretic, antimicrobial, antispasmodic, anti-inflammatory.
The use of cyston can be prescribed both as monotherapy and in combination with additional drugs for urolithiasis and other ailments of the urinary system. With ICD in complex therapy appoint a daily intake of cyston 2 tablets 2-3 times. Treatment can last up to six months or until the stones come out.
The composition of the Polish preparation phytolysin includes terpenes and other essential oils containing flavin, saponins, inositols, glycosides (sage, pine needles, peppermint), extracts of parsley seeds, birch leaves, horsetail grass, wheatgrass rhizomes, etc.) antispasmodic, bacteriostatic, diuretic action. It has an excellent anti-relapse effect after surgery. One teaspoon of paste, diluted with 100 ml of sweetish water, is consumed 3-4 times a day. With long-term use of this drug, a negative effect on the body was not observed.
The German drug nieron contains tincture of dental ammonia, madder dye, steel field, calendula, oxalic acid. It improves the process of blood supply to the kidneys, muscles, has an enhancing effect on the peristalsis of the urinary tract, has a diuretic and bacteriostatic effect. Nieron is used up to 3 times a day, 30-35 drops for 1-2 months. In the postoperative period, nieron is prescribed as an anti-relapse and anti-inflammatory agent.
Kanephron improves the state of the body as a whole, promotes increased output of urate stones, improves the general indicators of urine analysis, phosphorus-calcium metabolism, creatinine, reduces the permeability of blood vessels, enhances the effect of antibiotics. The therapeutic effect of canaferon is due to the extracts of centaury, lovage, wild rose, rosemary, ascorbic, citric, pectin and malic acids, vitamins included in its composition.
Back to the table of contents
Herbal treatment
Herbal preparations are an important part of complex therapy and preventive measures for the occurrence of urolithiasis. An antiseptic, antispasmodic, diuretic effect on urinary tract stones is exerted by phyto-assemblies, which in their composition contain: roots of parsley, madder dye, horsetail, steel, juniper berries, rose hips, peppermint leaves, stinging nettle and other plant components. It is important to know that some herbal infusions should not be taken with glomerulonephritis.
Back to the table of contents
Preventive actions
Urolithiasis is prone to recurrence, so preventive measures are very important. At the initial diagnosis, it is necessary to find out the nature of the stones formed in the urinary system. Thanks to this, it is possible to adjust nutrition, as well as to prescribe anti-relapse, prophylactic drug treatment.
With urolithiasis, stones (calculi) are formed in the organs of the urinary system.
This disease is detected in almost half of patients who seek medical help from a nephrologist or urologist.
The formation of stones in the organs of the genitourinary system
Most often, calculi form in the kidneys, but they can also occur in the ureters, bladder and urethra.
The course of the disease largely depends on the general condition of the patient, his lifestyle, the presence of concomitant pathologies.
In order to correctly choose a medicine for the treatment of urolithiasis, you need to know the exact size, location and cause of calculus formation.
Reasons for the formation of stones
Stones in the kidneys
Urolithiasis is a disease of the whole organism, and the formation of stones is only its consequence. This process is influenced by both endogenous and exogenous factors.
The endogenous causes of the development of urolithiasis include:
hypercalciuria, hypovitaminosis of vitamins A and D, overdose of calcium preparations; bacterial infection with pyelonephritis or glomerulonephritis; prolonged immobility after injury; high doses of certain drugs, such as sulfonamides, tetracycline antibiotics, antacids, aspirin, vitamin C, glucocorticoids; various diseases urinary system, which lead to impaired urodynamics (for example, nephroptosis, infections, neurogenic disorders of urinary outflow, vesicoureteral reflux); systemic metabolic disorders.
Exogenous causes are a person's lifestyle (more often stones are formed during physical inactivity), the composition and volume of drinking water consumed, and the diet.
With urolithiasis, calculi are formed from a variety of salts and minerals. The generally accepted classification is based on the predominance of one or another element.
Most often, the formation of calcium oxolate and calcium phosphate stones occurs, less often - urate, cystine, xanthine and cholesterol stones.
Oxalate stones
Oxolate calculi are formed when there is a violation of the excretion of oxolates in the urine. It can be caused by inflammatory processes in the intestines, prolonged diarrhea.
These stones are dark in color with sharp edges.
In bacterial inflammatory processes, the formation of phosphate stones occurs. They acquire a white or gray tint, easily disintegrate.
The risk of urate calculi formation is high with gout, cancer treatment as a side effect of chemotherapeutic agents. The main reason for the formation is the constant low pH value of urine.
They account for about 7% of cases of urolithiasis. They are usually brick-colored with a smooth surface.
As a result of impaired absorption of essential amino acids (cystine, ornithine, lysine and arginine), their level in urine increases.
Compared to other amino acids, cystine is practically insoluble in water and precipitates. Cystine calculi are subsequently formed from it.
Xanthine stones are extremely rare in congenital enzyme deficiency. Cholesterol - with systemic disorders of cholesterol metabolism.
If urolithiasis is diagnosed, then it is possible to determine the nature of the stone with the usual clinical analysis of urine.
Each type of calculus has a specific pH value.
Sometimes calculi can form in the bladder. This usually occurs in children and the elderly.
Symptoms
The size, shape, number and location of stones affect the manifestations of urolithiasis.
If they have a smooth surface, do not injure the mucous membrane and do not interfere with the outflow of urine, then they can only be accidentally detected during an ultrasound examination of the kidneys and other organs of the urinary system.
Pain after exercise
Usually, the first manifestation of urolithiasis is renal colic. It is caused by a violation of the outflow of urine from the kidney.
Obstruction of the ureter occurs due to blockage of the stone. In addition, the increased salt content in the urine causes muscle spasm of its walls.
An attack of renal colic usually begins after shaking, running, jumping, lifting weights, physical exertion.
Suddenly there is a sharp unbearable pain in the kidney area. It can give along the ureter to the perineum, inner thigh or leg.
Sharp pain
The pain syndrome is so strong that a person cannot tolerate it. He constantly changes his body position in an attempt to relieve pain.
When a stone enters the ureter, it injures the inner mucous membrane of its walls. Therefore, blood may appear in the urine.
Very often, renal colic is accompanied by nausea, vomiting, and fever.
For a while, the pain subsides with a change in the position of the stone, restoration of the outflow of urine. Renal colic completely disappears when the stone leaves the body.
Urolithiasis with localization of calculi in the bladder is accompanied by pain in the lower abdomen, especially when walking, physical exertion.
Therefore, symptoms usually appear during the daytime. A characteristic sign is a sharp interruption of urination. The manifestations of the disease are weakened when the patient takes a horizontal position.
Diagnostics
To choose the right treatment, the necessary medications, to determine whether antibiotics are needed, the timely diagnosis of urolithiasis will help.
Usually they start with a complete blood count. When a bacterial infection is attached, the ESR and the level of leukocytes increase. Urine analysis is more informative.
Laboratory diagnostics
Determine the pH level, the presence of bacteria, leukocytes, salts. In case of damage to the walls of the ureter and Bladder detect erythrocytes and transitional epithelium cells.
Diagnostics
To determine the localization, shape and size of the stone, ultrasound is most often performed. The value of this research method lies in the simplicity of its implementation, the absence of contraindications.
In addition, with an ultrasound examination, it is possible to assess general state kidneys and the entire urinary system.
X-ray examinations are done to confirm the diagnosis. Conventional X-ray is not very informative, therefore, to obtain a clearer picture, X-ray contrast agents are injected.
This method is called excretory urography. The images obtained make it possible to assess the size of the stone, its movement along the urinary tract, the functional ability of the kidneys and bladder.
Computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging is usually done before surgery is performed.
Treatment
Since often the first sign of urolithiasis is an attack of renal colic, all efforts are aimed at stopping it. After the patient's condition has improved, further treatment is carried out.
Drug treatment
To facilitate the passage of the stone through the urinary tract, drugs are prescribed to relieve spasm of smooth muscles. First of all, it is baralgin.
The use of this medication is most effective, as it additionally has an analgesic effect. No-shpa and glucagon have an excellent antispasmodic effect on the muscles of the ureters.
Progesterone preparations also reduce the tone of the urinary tract.
Certain hormones (such as adrenaline and norepinephrine) increase smooth muscle spasms. To block their action, special drugs of the adrenergic blocking group are used.
Hormone therapy
These are drugs such as doxazosin, terazosin, alfuzosin.
The neurotransmitter acetylcholine acts selectively. It causes muscle contraction in all organs except the urinary system. Here its effect is exactly the opposite.
Medicines of the cholinomimetic group enhance its effect. These are hyoscine methyl bromide, atropine, spasmocysthenal.
To stop the inflammatory process, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are used. These are ketorolac, diclofenac, less often acetylsalicylic acid.
Prescribing pain relievers is mandatory. They are divided into two large groups, which differ in the strength of the analgesic effect.
These are non-narcotic analgesics (analgin, paracetamol, ibuprofen, nimesil) and narcotic (tramadol, omnopon, morphine, codeine). With severe pain syndrome, drugs from the second group are used.
Sometimes a local novocaine or lidocaine blockade is performed.
If an attack of renal colic is accompanied by vomiting, then the drug metoclopramide is additionally used.
Catheterization
In order to reduce the formation of urine, medications such as desmopressin, minirin, presinex or emosynt are taken.
In an emergency, a combination of drugs is administered. This is usually an antispasmodic and anti-inflammatory medication. Then, based on the patient's condition, add analgesics, antiemetics.
In severe cases, urine diversion is carried out using a catheter.
Usually, pills can be taken outside of an attack instead of injecting drugs.
After stopping renal colic, a comprehensive examination of the patient is carried out. Based on its results, further treatment of urolithiasis is determined.
If the size of the stones is small, and they can painlessly leave the kidney, then a combination of drugs is prescribed.
They improve renal blood circulation, increase urine output, relieve spasm of the urinary tract and enhance their peristalsis, prevent the development of bacterial complications.
Usually used:
enatin or olimetin are herbal preparations that have antispasmodic, diuretic and anti-inflammatory effects; rovatinex, the drug increases renal blood flow, has an antispasmodic, anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial effect; cyston, these tablets have anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial effects; phytolysin not only has antimicrobial, bacteriostatic and anti-inflammatory effects, but also loosens stones, facilitates their exit from the kidneys; palin is an antibacterial medicine.
Urate stones dissolve well with prolonged use of drugs such as uralit-U, blemaren, margulite. These medicines not only contribute to the dissolution of calculi, but also prevent their further formation.
Calculi
It is necessary to take these drugs for about 2 - 3 months. This requires regular monitoring of the urine pH level. It should not exceed 7.0.
A very serious complication of urolithiasis is bacterial inflammation of the kidneys - pyelonephritis. It is characterized by a sharp rise in temperature, aching pain in the lumbar region.
Antibiotics are used to treat this disease. Usually, the causative agents of pyelonephritis are E. coli and Pseudomonas aeruginosa, streptococci, staphylococci.
Therefore, antibacterial drugs are chosen taking into account their effect on these groups of microorganisms.
For infectious complications of urolithiasis, the following antibiotics are effective:
cephalosporins of the third and fourth generations (ceftriaxone, sulfactam, cefotaxime, ceftazidime); fluoroquinolones (levofloxacin, sparfloxacin, moxifloxacin); sulfonamides (biseptol); penicillins (amoxiclav, ampicillin, piperatsilin).
Antibiotic treatment
Antibiotic use usually lasts up to two weeks. In combination with these drugs, it is necessary to use drugs to restore the intestinal microflora. These are linex, bio-gaya, bifidumbacterin or bactisubtil.
After the end of the course of therapy with antibacterial agents, uroseptic drugs are prescribed. These are drugs such as urolesan, kanefron, furagin.
They need to be taken over a long period of time, possibly several months. The duration of treatment is determined by the attending physician.
Herbal medicine is also very useful: decoctions of lingonberry leaves, bearberry, birch, half-fallen grass, kidney tea, horsetail, chamomile flowers, calendula.
In addition to drugs, there are also instrumental methods of treating urolithiasis.
If the stones lend themselves well to dissolution, then special drugs are injected directly into the kidney through a catheter.
Such treatment is carried out if the size of the stones does not exceed 5 mm, and they do not interfere with the normal functioning of the kidney.
Insoluble calculi are removed with instruments that are inserted into the urethra, bladder, or ureter through a catheter. These manipulations are carried out under the control of ultrasound.
The method of remote shock wave lipotripsy consists in the destruction of the stone shock wave... This method of therapy lends itself to stones up to 2 cm in size.
There are contraindications to such a procedure.
These are overweight, diseases of the musculoskeletal system and the cardiovascular system, pregnancy, an acute infectious process in the genitourinary system, and impaired urine outflow.
In severe urolithiasis, laparoscopic surgical treatment is indicated.
With urolithiasis, stones (calculi) are formed in the organs of the urinary system.
This disease is detected in almost half of patients who seek medical help from a nephrologist or urologist.
The formation of stones in the organs of the genitourinary system
Most often, calculi form in the kidneys, but they can also occur in the ureters, bladder and urethra.
The course of the disease largely depends on the general condition of the patient, his lifestyle, the presence of concomitant pathologies.
In order to correctly choose a medicine for the treatment of urolithiasis, you need to know the exact size, location and cause of calculus formation.

Stones in the kidneys
Urolithiasis is a disease of the whole organism, and the formation of stones is only its consequence. This process is influenced by both endogenous and exogenous factors.
The endogenous causes of the development of urolithiasis include:
- hypercalciuria, hypovitaminosis of vitamins A and D, overdose of calcium preparations;
- bacterial infection with pyelonephritis or glomerulonephritis;
- prolonged immobility after injury;
- large doses of certain drugs, such as sulfonamides, tetracycline antibiotics, antacids, aspirin, ascorbic acid, glucocorticoids;
- various diseases of the urinary system that lead to impaired urodynamics (for example, nephroptosis, infections, neurogenic disorders of urinary outflow, vesicoureteral reflux);
- systemic metabolic disorders.
Exogenous causes are a person's lifestyle (more often stones are formed during physical inactivity), the composition and volume of drinking water consumed, and the diet.
With urolithiasis, calculi are formed from a variety of salts and minerals. The generally accepted classification is based on the predominance of one or another element.
Most often, the formation of calcium oxolate and calcium phosphate stones occurs, less often - urate, cystine, xanthine and cholesterol stones.

Oxalate stones
Oxolate calculi are formed when there is a violation of the excretion of oxolates in the urine. It can be caused by inflammatory processes in the intestines, prolonged diarrhea.
These stones are dark in color with sharp edges.
In bacterial inflammatory processes, the formation of phosphate stones occurs. They acquire a white or gray tint, easily disintegrate.
The risk of urate calculi formation is high with gout, cancer treatment as a side effect of chemotherapeutic agents. The main reason for the formation is the constant low pH value of urine.
They account for about 7% of cases of urolithiasis. They are usually brick-colored with a smooth surface.
As a result of impaired absorption of essential amino acids (cystine, ornithine, lysine and arginine), their level in urine increases.
Compared to other amino acids, cystine is practically insoluble in water and precipitates. Cystine calculi are subsequently formed from it.
Xanthine stones are extremely rare in congenital enzyme deficiency. Cholesterol - with systemic disorders of cholesterol metabolism.
If urolithiasis is diagnosed, then it is possible to determine the nature of the stone with the usual clinical analysis of urine.
Each type of calculus has a specific pH value.
Sometimes calculi can form in the bladder. This usually occurs in children and the elderly.
Symptoms
The size, shape, number and location of stones affect the manifestations of urolithiasis.
If they have a smooth surface, do not injure the mucous membrane and do not interfere with the outflow of urine, then they can only be accidentally detected during an ultrasound examination of the kidneys and other organs of the urinary system.

Pain after exercise
Usually, the first manifestation of urolithiasis is renal colic. It is caused by a violation of the outflow of urine from the kidney.
Obstruction of the ureter occurs due to blockage of the stone. In addition, the increased salt content in the urine causes muscle spasm of its walls.
An attack of renal colic usually begins after shaking, running, jumping, lifting weights, physical exertion.
Suddenly there is a sharp unbearable pain in the kidney area. It can give along the ureter to the perineum, inner thigh or leg.

Sharp pain
The pain syndrome is so strong that a person cannot tolerate it. He constantly changes his body position in an attempt to relieve pain.
When a stone enters the ureter, it injures the inner mucous membrane of its walls. Therefore, blood may appear in the urine.
Very often, renal colic is accompanied by nausea, vomiting, and fever.
For a while, the pain subsides with a change in the position of the stone, restoration of the outflow of urine. Renal colic completely disappears when the stone leaves the body.
Urolithiasis with localization of calculi in the bladder is accompanied by pain in the lower abdomen, especially when walking, physical exertion.
Therefore, symptoms usually appear during the daytime. A characteristic sign is a sharp interruption of urination. The manifestations of the disease are weakened when the patient takes a horizontal position.
Diagnostics
To choose the right treatment, the necessary medications, to determine whether antibiotics are needed, the timely diagnosis of urolithiasis will help.
Usually they start with a complete blood count. When a bacterial infection is attached, the ESR and the level of leukocytes increase. Urine analysis is more informative.

Laboratory diagnostics
Determine the pH level, the presence of bacteria, leukocytes, salts. In case of damage to the walls of the ureter and bladder, erythrocytes and transitional epithelium cells are found.

Diagnostics
To determine the localization, shape and size of the stone, ultrasound is most often performed. The value of this research method lies in the simplicity of its implementation, the absence of contraindications.
In addition, with an ultrasound examination, it is possible to assess the general condition of the kidneys and the entire urinary system.
X-ray examinations are done to confirm the diagnosis. Conventional X-ray is not very informative, therefore, to obtain a clearer picture, X-ray contrast agents are injected.
This method is called excretory urography. The images obtained make it possible to assess the size of the stone, its movement along the urinary tract, the functional ability of the kidneys and bladder.
Computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging is usually done before surgery is performed.
Treatment
Since often the first sign of urolithiasis is an attack of renal colic, all efforts are aimed at stopping it. After the patient's condition has improved, further treatment is carried out.

Drug treatment
To facilitate the passage of the stone through the urinary tract, drugs are prescribed to relieve spasm of smooth muscles. First of all, it is baralgin.
The use of this medication is most effective, as it additionally has an analgesic effect. No-shpa and glucagon have an excellent antispasmodic effect on the muscles of the ureters.
Progesterone preparations also reduce the tone of the urinary tract.
Certain hormones (such as adrenaline and norepinephrine) increase smooth muscle spasms. To block their action, special drugs of the adrenergic blocking group are used.

Hormone therapy
These are drugs such as doxazosin, terazosin, alfuzosin.
The neurotransmitter acetylcholine acts selectively. It causes muscle contraction in all organs except the urinary system. Here its effect is exactly the opposite.
Medicines of the cholinomimetic group enhance its effect. These are hyoscine methyl bromide, atropine, spasmocysthenal.
To stop the inflammatory process, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are used. These are ketorolac, diclofenac, less often acetylsalicylic acid.
Prescribing pain relievers is mandatory. They are divided into two large groups, which differ in the strength of the analgesic effect.
These are non-narcotic analgesics (analgin, paracetamol, ibuprofen, nimesil) and narcotic (tramadol, omnopon, morphine, codeine). With severe pain syndrome, drugs from the second group are used.
Sometimes a local novocaine or lidocaine blockade is performed.
If an attack of renal colic is accompanied by vomiting, then the drug metoclopramide is additionally used.

Catheterization
In order to reduce the formation of urine, medications such as desmopressin, minirin, presinex or emosynt are taken.
In an emergency, a combination of drugs is administered. This is usually an antispasmodic and anti-inflammatory medication. Then, based on the patient's condition, add analgesics, antiemetics.
In severe cases, urine diversion is carried out using a catheter.
Usually, pills can be taken outside of an attack instead of injecting drugs.
After stopping renal colic, a comprehensive examination of the patient is carried out. Based on its results, further treatment of urolithiasis is determined.
If the size of the stones is small, and they can painlessly leave the kidney, then a combination of drugs is prescribed.
They improve renal blood circulation, increase urine output, relieve spasm of the urinary tract and enhance their peristalsis, prevent the development of bacterial complications.
Usually used:
- enatin or olimetin are herbal preparations that have antispasmodic, diuretic and anti-inflammatory effects;
- rovatinex, the drug increases renal blood flow, has an antispasmodic, anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial effect;
- cyston, these tablets have anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial effects;
- phytolysin not only has antimicrobial, bacteriostatic and anti-inflammatory effects, but also loosens stones, facilitates their exit from the kidneys;
- palin is an antibacterial medicine.
Urate stones dissolve well with prolonged use of drugs such as uralit-U, blemaren, margulite. These medicines not only contribute to the dissolution of calculi, but also prevent their further formation.

It is necessary to take these drugs for about 2 - 3 months. This requires regular monitoring of the urine pH level. It should not exceed 7.0.
A very serious complication of urolithiasis is bacterial inflammation of the kidneys - pyelonephritis. It is characterized by a sharp rise in temperature, aching pain in the lumbar region.
Antibiotics are used to treat this disease. Usually, the causative agents of pyelonephritis are E. coli and Pseudomonas aeruginosa, streptococci, staphylococci.
Therefore, antibacterial drugs are chosen taking into account their effect on these groups of microorganisms.
For infectious complications of urolithiasis, the following antibiotics are effective:
- cephalosporins of the third and fourth generations (ceftriaxone, sulfactam, cefotaxime, ceftazidime);
- fluoroquinolones (levofloxacin, sparfloxacin, moxifloxacin);
- sulfonamides (biseptol);
- penicillins (amoxiclav, ampicillin, piperatsilin).

Antibiotic treatment
Antibiotic use usually lasts up to two weeks. In combination with these drugs, it is necessary to use drugs to restore the intestinal microflora. These are linex, bio-gaya, bifidumbacterin or bactisubtil.
After the end of the course of therapy with antibacterial agents, uroseptic drugs are prescribed. These are drugs such as urolesan, kanefron, furagin.
They need to be taken over a long period of time, possibly several months. The duration of treatment is determined by the attending physician.
Herbal medicine is also very useful: decoctions of lingonberry leaves, bearberry, birch, half-fallen grass, kidney tea, horsetail, chamomile flowers, calendula.
In addition to drugs, there are also instrumental methods of treating urolithiasis.
If the stones lend themselves well to dissolution, then special drugs are injected directly into the kidney through a catheter.
Such treatment is carried out if the size of the stones does not exceed 5 mm, and they do not interfere with the normal functioning of the kidney.
Insoluble calculi are removed with instruments that are inserted into the urethra, bladder, or ureter through a catheter. These manipulations are carried out under the control of ultrasound.
The method of distance shock wave lipotripsy consists in the destruction of the stone by a shock wave. This method of therapy lends itself to stones up to 2 cm in size.
There are contraindications to such a procedure.
These are overweight, diseases of the musculoskeletal system and the cardiovascular system, pregnancy, an acute infectious process in the genitourinary system, and impaired urine outflow.
In severe urolithiasis, laparoscopic surgical treatment is indicated.
Kidney stones are very painful. To get rid of them, it is necessary to use medications for kidney stones. Modern drugs allow you to remove small stones by dissolving them. For the treatment of urolithiasis, drugs, mineral waters and folk remedies are used.
Traditional drugs
Solid deposits (stones) in the kidneys are formed as a result of a violation of the acid-base balance and the metabolic process in the body. It should be noted that certain preparations intended for dissolving stones should be used only for a certain type of kidney stones. If the patient does not adhere to this rule or independently changes the dose of the drug, then the violation of the acid-base balance changes even more in one direction or another. This process will lead to an increase in the size of existing stones or the formation of new ones.
- Allopurinol is a drug that helps fight various types of calculus. The components of the drug help to reduce the concentration of uric acid.
- Asparkam - helps to get rid of oxalates and urates. The drug affects the heart, so it must be taken with great care. Asparkam is considered one of the most effective drugs.
- Blemaren is a drug that dissolves oxalates in the kidneys and bladder. The drug helps to alkalize the urine.
- Dye madder extract is a plant extract that can be used to dissolve phosphate stones. While taking the drug, urine turns red, which frightens patients, but this is not blood, but an extract of madder.
- Cyston - helps dissolve oxalate calculi. The drug can also be used to dissolve hard stones of a different composition, while the acid-base balance of urine does not change.
The above drugs are available in pill form. Also, preparations are used in the form of a solution and a paste. Among them are:
- Ksidifon is a medicinal solution that is taken by mouth. Helps dissolve phosphate and oxalate kidney stones.
- Urolesan - drops, they help to remove solid deposits from the kidneys due to the antispasmodic and diuretic effect.
- Phytolysin is a paste that gradually destroys kidney stones, flushing out their inner part. Oxalate becomes sieve-like and then breaks down.
When removing stones, it is necessary to use not only drugs that promote destruction, but also means that help remove stones through the urinary tract. Therefore, the treatment regimen should include a set of remedies. All medications must be prescribed by a doctor; self-treatment can worsen health.
ARVE Error:
Mineral water as a remedy against stones
Many urologists believe that mineral water helps dissolve stones. Water is selected based on the type of solid deposits in the kidneys. The intake and dosage of mineral water should be prescribed by the attending physician, because its uncontrolled use can lead to the leaching of useful substances and disrupt the functioning of the kidneys. Each mineral water has a number that determines its alkalinity. There are the following main types of mineral water:
- medicinal alkaline mineral water - helps to dissolve oxalates and uratates (Polyana Kvasovaya, Borzhomi, Essentuki 17);
- mineral water with high acidity - used in the presence of phosphates (Narzan, Mirgorodskaya).
ARVE Error: id and provider shortcodes attributes are mandatory for old shortcodes. It is recommended to switch to new shortcodes that need only url
Treatment with folk methods
You can cure urolithiasis with the help folk remedies, but only if the disease is at an early stage, while the formations are small. The following folk remedies can be distinguished:
- When renal colic appears, it is recommended to use strawberry leaves. 100 g of leaves (or berries) pour 1 liter of boiling water. The dishes in which the leaves are brewed should be tightly wrapped with a warm towel for 24 hours, then filtered. Take 200 ml 2 times a day with meals for 7 days. After that, a break is made for 3 days and the course is repeated. No more than 4-5 courses of treatment are allowed.
- Fresh cranberries help dissolve stones and remove sand from the genitourinary system. 100 g of cranberries are poured into 1 liter of boiling water and insisted for 5 hours. The medicine is taken once a day for 30 days.
- Birch juice. It is necessary to drink 200 ml of birch sap every morning on an empty stomach. At lunchtime after meals, you should drink 2 tbsp. l. olive oil, and before bedtime another 200 ml of birch sap.
- Infusion of birch buds. 2 tbsp. l. the kidneys should be poured with 500 ml of boiling water and insisted for 24 hours. After that, the agent is filtered and taken in 100 ml daily, 2 times a day. The infusion helps to relieve pain, therefore, after they are eliminated, the intake of the drug must be suspended.
- Flax seed infusion. It has an analgesic effect. Pour 100 g of seeds into 1 liter of water and boil over low heat for 1 hour. The infusion is taken at 500 ml per day.
- Decoction of burdock root. 2 tbsp. l. root, pour 500 ml of boiling water and boil in a water bath for 30 minutes. The tool is taken 3 times a day, 100 ml before meals.
Traditional and alternative medicine offers a wide range of remedies for the treatment of urolithiasis, but only a specialist should prescribe them.
Urolithiasis requires careful and competent selection of drugs, should be based on accurate diagnosis with the definition of the type, size and location of crystalline formations, analysis of the composition of urine and blood. Medicines prescribed by a specialist are designed to improve the advancement of calculi along the urinary system, their dissolution, and should also help prevent the formation of new kidney stones.
Medicines for the treatment of urolithiasis
Urolithiasis (nephrolithiasis) is a fairly common pathology that affects the kidneys. It is characterized by the formation of stones in the organs of the urinary system. The pathology treatment regimen may include the use of antispasmodics, diuretics, analgesics, antibiotics. On initial stages and complex herbal preparations are effective for prevention, but in serious cases they only supplement potent synthetic agents.
Drug therapy is indicated if the size of the stone does not exceed 0.5 cm
Drug therapy is indicated when the size of the crystals in the kidneys is up to 0.5 cm, so that the particles are expelled under the action of drugs, without causing overlap of the kidney cavities.
When treatment displaces large masses, they become stuck in the ducts and cause an attack acute pain- renal colic. This is accompanied by a violation of the outflow of urine. The consequences of this condition: painful stone exit with damage to the walls of the urinary tract or the need for surgery. Therefore, medications for urolithiasis can be taken only on the recommendation of a urologist, under the supervision and after a complete diagnosis.
Pain relievers
Drugs in this group act by relieving spasms or reducing sensitivity. To enhance the effect, they are combined, but only as directed by a doctor. Such funds are needed for acute pain that occurs during renal colic, therefore, are mandatory for a home first-aid kit for a patient with urolithiasis.
Intramuscular or intravenous injections stop the attack more quickly. If you cannot get an injection, take the pills. They are also used to relieve pain of moderate to low intensity.
 With obstruction of the pelvis, a strong analgesic can distort the picture of the disease and cause a misdiagnosis
With obstruction of the pelvis, a strong analgesic can distort the picture of the disease and cause a misdiagnosis These drugs relieve spasms of the walls of blood vessels and urinary tract, block pain receptors, which are irritated by the pressure of stones, and especially strongly when shifting during renal colic.
Table: drugs for pain relief for renal colic
| Drug, country | Forms of issue | Active ingredients | Indications | Description of the drug, action | |
| Papaverine (Russia, Belarus, Moldova) |
| antispasmodic papaverine hydrochloride | renal colic |
| Quickly relieves pain, it can even be taken by lactating and pregnant women, but not systematically, since the drug belongs to the drug group. |
| Platyphyllin (Ukraine) |
| pain receptor blocker platyphylline hydrotartrate |
| It has an antispasmodic and mild sedative effect. The medicine is combined with Papaverine, but it has many contraindications. You must not drive a car after the appointment. | |
| No-shpa (Hungary); Drotaverin (Russia, Belarus) |
| antispasmodic drotaverine hydrochloride | moderate pain in the lumbar region caused by spasm |
| Relieves spasms, reduces inflammation and swelling without blocking pain receptors, this makes diagnosis easier. |
| Analgin (Russia, Belarus) |
| analgesic metamizole sodium |
|
| It helps with pains of no higher than average intensity, in case of colic, an injection is given in combination with Diphenhydramine. |
| Spazdolzin (Germany) | candles:
| metamizole sodium | renal colic | Analgesic agent. It is used when oral medication is difficult or undesirable. | |
| Spazmalgon (Bulgaria) | 500 mg tablets: 5 mg: 100 mcg |
| mild to moderate pain syndrome |
| It has a relaxing, analgesic and antipyretic effect. |
| Maxigan India | |||||
| Baralgin (India) |
|
||||
| Ketanov (India) | tablets 10 mg | analgesic ketorolac tromethamine | short-term relief of severe and moderate pain |
| It is a powerful non-narcotic analgesic and is recommended for adults only. |
| Diclofenac (Russia, Moldova, Belarus, Cyprus, Romania) |
| analgesic diclofenac sodium | for the short-term reduction of pain and inflammation in colic |
| Relieves pain and inflammatory edema for a short time. |
Prescribing antibiotics for kidney stones
Antimicrobial therapy is practiced for infectious complications and the detection of struvite stones, which are formed under the action of Escherichia coli, staphylococci and enterococci. When prescribing drugs, the following rules are observed:
- make sure that the patient does not have an impaired outflow of urine, otherwise bacteriotoxic shock develops against the background of the action of antibiotics;
- prescribe a course of treatment for at least a week;
- groups of drugs are thoughtfully combined, since many drugs are incompatible: the simultaneous administration of bactericidal cephalosporins, carbapenems, aminoglycosides, fluoroquinolones with bacteriostatic tetracycline and doxycycline leads to their mutual deactivation.
As long as the stones remain in the kidneys, it is impossible to completely get rid of the infection, therefore antibiotic therapy is used before and after the removal of calculus.
 Cephalosporins have greater antimicrobial activity than antibiotics of other groups
Cephalosporins have greater antimicrobial activity than antibiotics of other groups With a strong inflammatory process, the following groups of antimicrobial agents are used:
- cephalosporins of the third (Ceftazidime, Ceftriaxone) and fourth generation (Cefepim) are broad-spectrum drugs with increased bactericidal activity and low toxicity;
- carbapenems (Meropenem, Imipenem + Cilastatin) - act on most bacteria, but taking them longer than 7 days can lead to enterocolitis;
- fluoroquinolones II (Ciprofloxacin, Ofloxacin, Lomefloxacin), III (Levofloxacin), IV generation (Gatifloxacin) - are used to combat aerobic bacteria (Shigella, Staphylococcus, Pseudomonas aeruginosa);
- aminoglycosides (Gentamicin, Amikacin) - have a limited effect, are highly toxic, many microorganisms are resistant to them.
With minor inflammation, nitrofurans (Furazolidone, Furazidin) are prescribed, which allow you to get rid of concomitant infections that complicate the course of urolithiasis in time.
 Furazolidone will be effective for minor inflammation
Furazolidone will be effective for minor inflammation Table: antibiotics used in the treatment of urolithiasis
| Drug, country of origin | Forms used for urolithiasis, composition | Active ingredients | Indications | Contraindications other than hypersensitivity |
| Ceftazidime (Russia, India, Belarus) | powder of 2000 mg in vials, diluted to obtain an injection solution | ceftazidime | severe infections with an unknown underlying cause | no, except for intolerance to penicillins and cephalosporins, careful use for pregnant and lactating women, newborns |
| vials, 500 or 1000 mg powder | ceftriaxone sodium salt |
|
|
| Cefepim (Russia, China, Belarus) | cefepime hydrochloride |
|
||
| Carbapenems | ||||
| Meropenem (Russia, India, Belarus, Kazakhstan, Switzerland) | vials, powder 1000 or 500 mg | meropenem trihydrate | infectious and inflammatory pathologies of the kidneys with an undefined pathogen |
|
| Imipenem + Cilastatin (India) | powder vials, 500 mg of each active ingredient |
|
|
|
| Fluoroquinolones (with rare exceptions cannot be taken during pregnancy and lactation, under 18 years of age) |
||||
| Ofloxacin (Russia) |
| ofloxacin | kidney infections caused by aerobic bacteria; including in children, pregnant and lactating for the treatment of anthrax and Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection | pathology and brain injury |
| tablets 400 mg | lomefloxacin | age up to 15 years | |
| Ciprofloxacin (Russia, India) |
| ciprofloxacin hydrochloride monohydrate |
|
|
|
| levofloxacin hemihydrate | complicated urinary tract infections |
|
|
| gatifloxacin | diabetes | |
| Aminoglycosides | ||||
| Amikatsin (Russia, Belarus) |
| amikacin sulfate | urinary tract infections with frequent relapses caused by drug-sensitive microbes |
|
| Gentamicin (Russia, Belarus) | powder vials 80 mg | gentamicin sulfate | ||
| Nitrofurans | ||||
| Furazolidone (Russia, Belarus) |
| furazolidone | accompanying urolithiasis cystitis, urethritis, complications after removal of stones |
|
|
| furazidine |
|
|
| tablets 50, 100 mg | ||||
Diuretic drugs
Diuretics are not used to treat children under 12 years of age and with stones up to 5 mm. If particles smaller than the specified size are found in the kidneys, the selection of a urinary enhancer for their expulsion is determined by the composition of the stones.

Table: Diuretics for the removal of small stones
| A drug | Forms that are used for urolithiasis, the content of the active substance | Active substances | Indications for urolithiasis | Contraindications other than hypersensitivity |
| tablets 25 mg | spironolactone | phosphate or calcium stones |
|
| Aldactone (USA) | tablets 25, 100 mg |
Complex herbal preparations
A smart alternative to herbal preparations - multicomponent formulations with precise dosage and a balanced combination of active substances of natural origin.
Differences from synthetic products:
- gently affect the body, the side effects are weaker;
- more often suitable for children, pregnant and lactating women;
- are treated in a complex, at the same time as pain relievers, anti-inflammatory, bactericidal, diuretic and dissolving agents.
Dozens of components increase the likelihood of allergies, individual intolerance, side effects, and unwanted interactions with other medications. Therefore, the appointment and supervision of a doctor in the treatment of urolithiasis with natural preparations and herbal preparations are necessary. Such medications are used as a supplement to treatment with synthetic drugs, or as a continuation of antimicrobial therapy after the completion of antibiotics.
All complex herbal preparations shown for urolithiasis have a moderate antimicrobial, antispasmodic, diuretic, litholytic (stone-dissolving) effect, which manifests itself when taken systematically by the recommended courses. The visible effect appears in 12-15 days from the beginning and lasts 2-4 weeks after the end of therapy. When treating with these remedies, they drink a lot of fluids.
Table: combined herbal remedies for the treatment of KSD
| Drug, country of origin | Release form | Composition | Indications | Contraindications | Description of the drug, action |
| Kanefron (Germany) |
| extracts of lovage, wild rose, centaury, rosemary |
|
| It removes urates, does not wash out potassium. In case of exacerbation, it will not replace strong drugs, but can supplement them. Includes only 4 plants, so the likelihood of allergies is not high. Can be prescribed during pregnancy and lactation. Contains vitamin C, carotene, essential oils and flavonoids with a diuretic and antispasmodic effect. |
| Cyston (India) | pills |
|
|
| The effect is similar to Canephron, but the antimicrobial effect is more pronounced. It contains 15 active ingredients, 13 of them are plants, which increases the chances of allergies. Covers prickly crystals with a soft film, which makes their removal less painful. |
| Cistenal (Germany) | vials 10 ml |
|
|
| Loosens calcium and magnesium stones, due to the pronounced antispasmodic effect, helps with colic, and with regular use prevents it. |
| Fitolysin (Poland) | a paste of extracts and ethyl alcohol in a ratio of 1: 1.5 | in 100 g of the mixture:
|
|
| It differs from other drugs in pasty consistency. It is a mixture of 13 herbal ingredients with a pronounced urolytic and antimicrobial effect. |
| Enatin | oil solution | for 1 g of oil solution:
| prevention and treatment of urolithiasis |
| It activates the renal circulation, which accelerates the flow of urine and reduces inflammation. Due to the sulfur and turpentine oil content, it has many contraindications. |
Herbal preparations for urolithiasis: photo gallery
 Kanefron is a plant-based drug that removes urates
Kanefron is a plant-based drug that removes urates  Cyston - a treatment for nephrolithiasis vegetable origin
Cyston - a treatment for nephrolithiasis vegetable origin  Phytolysin is convenient to carry with you and to prepare solutions from it thanks to the packaging in a compact tube
Phytolysin is convenient to carry with you and to prepare solutions from it thanks to the packaging in a compact tube
Drugs that loosen, dissolve, and remove kidney stones
Medicines that are used to get rid of stones in the urinary system are called nephrourolitic drugs. Their choice is determined by the composition, shape, size, hardness and other features of the stones.
Urates - salts of uric acid - are loosened to a powder under the action of a citrate mixture, which changes the reaction of urine from acidic to slightly alkaline. This is a solution of 2 g of citric acid and 3.5 g of its sodium salt in 100 ml of distilled water, it is prepared according to a prescription in pharmacies and is drunk in courses of up to 2-6 months. There are similar German-made drugs:
- Uralit-U. Potassium and sodium hydrocitrate in granules. It is used to dissolve stones and prevent their formation. You can not drink with a salt-free diet, dysfunctions and infections of the liver and kidneys, alkalosis;
- Blemaren. Powder in granules or dissolving tablets. Dissolves and prevents the appearance of not only urate stones, but also oxalate, cystine and combined stones. Contains per 100 g: 39.9 g of citric acid, 27.856 g of potassium bicarbonate, 32.25 g of anhydrous trisodium citrate. Contraindications: renal failure, salt-free diet, acid-base metabolism disorders, urinary tract infections with pathogens that can break down urea, urine acidity above 7.
Non-citrate litholytics also belong to the counter-urate group:
- Allopurinol. Produced in Hungary and Ukraine. In tablets 100, 300 mg of active ingredient. It inhibits the enzymes that control the formation of uric acid, the stones gradually dissolve. Cannot be used for seizures, hepatic and renal dysfunctions, hemochromatosis. Analog - Hungarian Allupol;
- Allomaron (France). Helps to relieve not only of urates, but also of calcium oxalate formations. The tablet, in addition to 0.1 g of allopurinol, contains 0.02 g of benzbromarone. Does not apply until the age of 14, during pregnancy, lactation, hemochromatosis and severe nephropathologies
Oxalate and phosphate stones are dissolved with herbal preparations, herbs or dietary supplements.
Cystine formations are crushed and removed, Kuprenil (Poland) prevents their appearance. The tablet contains 250 mg of penicillamine. Contraindicated for children under 3 years of age, pregnant women, with violations of hematopoiesis, renal failure, agranulocytosis.
Small stones of any composition are expelled by the Russian drug Avisan, which causes significant relaxation of smooth muscles. Tablets of 50 mg from dental ammonium contain 8% of strong antispasmodics chromones. Take for colic. Contraindicated in renal and heart failure.
Since water is needed for dissolution, all stone-dissolving and expelling agents require a large amount of it - as directed by a doctor, up to 2 liters per day, not counting the liquid obtained with food intake.
Preparations for the removal of stones: photo gallery
 Allopurinol inhibits the enzymes that control the formation of uric acid
Allopurinol inhibits the enzymes that control the formation of uric acid  Blemaren dissolves and prevents urate, oxalate, cystine and combination stones
Blemaren dissolves and prevents urate, oxalate, cystine and combination stones  Cuprenil crushes and removes cystine formations
Cuprenil crushes and removes cystine formations  Uralit-U is used to dissolve stones and prevent their formation
Uralit-U is used to dissolve stones and prevent their formation
Video: how to apply Blemaren
Homeopathy and treatment of nephrourolithiasis
Alternative medicine offers a number of drugs that complement, but do not replace, certified remedies. Illusory therapy instead of real therapy can lead to enlargement of stones, increased infection and inflammation. The benefits of homeopathic medicines are not recognized by the WHO and the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation, it is dangerous to purchase them without a doctor's recommendation and not on the open market for the treatment of such a complex disease as urolithiasis.
 According to RIA Novosti, treatment with ultra-low doses is recognized in different European countries by 25 to 86% of doctors
According to RIA Novosti, treatment with ultra-low doses is recognized in different European countries by 25 to 86% of doctors Pharmacies offer drugs with a composition tested for toxicity:
- Berberis. The drops contain a 35% alcoholic solution of an extract of the bark of the roots of barberry, rhizomes of hellebore white, pulp of the fruit of the lemon-shaped colocynth. It is proposed as an anti-inflammatory and mild antispasmodic. Cannot be used under 18 years of age;
- Renelle. Sublingual tablets with extracts of common barberry, chondrodendron felt, serrata sawn, lead acetate, nitric acid, aluminum oxide, powder from the spanish fly, caustic soda. Influences microbial microflora. Contraindicated for up to 3 years, with violations of carbohydrate metabolism;
- Populus compositum. In the form of drops of 80% alcoholic solution of extract of poplar, serenia, paprika and cubeb, 14 more plants, bee venom, camphor oil, creosote, mercury chloride. Used as a decongestant, diuretic, to weaken intoxication with urolithiasis from the age of 18, in the absence of alcoholism, brain and liver diseases;
- Solidago compositum. Solution for intramuscular administration, contains extracts of goldenrod, barberry and 7 other plants, extracts from the pork bladder, pelvis, urethra, silver nitrate, copper and calcium sulfates, mercuric chloride. Diuretic and antispasmodic. From the age of 18.
Supplements for kidney stones
Dietary supplements are taken with food and added to products for enrichment with vitamins, minerals, and enzymes. They can be considered useful components of the diet, but not drugs. Many urological dietary supplements contain potent substances, have serious contraindications and side effects, so they cannot be taken without the recommendation of a nephrologist.
 Uroprofit, like other dietary supplements for the treatment of urolithiasis, is based on herbal collection
Uroprofit, like other dietary supplements for the treatment of urolithiasis, is based on herbal collection Russian pharmaceutical companies offer in pharmacy chains and through online stores additives of different spectrum of action and forms for the treatment of urolithiasis:
- Uroprofit. Vitamin C 35 mg, antimicrobial components of proangocyanidins 37, 75 mg, antiseptic arbutin 4 mg in one capsule. Contains extracts of cranberry, bearberry, horsetail. Acts as a uroantiseptic, diuretic, antispasmodic, immunostimulant, according to research results, it reduces the content of salts in urine in 30% and leukocytes in 50% of patients;
- Epam-96 M. Propolis emulsion and extracts from 11 herbs. Prevents the formation of new stones;
- Nephrovit. Altai honey syrup with 6 herbs. Reduces crystalluria, prevents the growth of calculi;
- Renon Duo. 3 types of capsules with different composition, 22 different extracts in the morning capsule, 31 in the day, 32 in the evening. Fights infections in urinary tract, reduces pain, contains vitamins. Indications - inflammatory complications in urolithiasis, removal of small calculi, prevention of the formation of new ones. For children under 12 years old, solutions are prepared from the contents of the capsules. Designed for a month course. Contraindicated in children under 2 years of age;
- The origins of purity # 1. Capsules with 17 herbs. Activates the cleansing function of the kidneys, recovery after a long course of antibiotics;
- Lymphosan U. Capsules with wheat and oat bran contain 9 herbs. It is offered for use from 12 years old as a mild diuretic and an adsorbent of toxins accumulated in the kidneys;
- Lymphosan M and Zh. Includes wheat and oat bran, 11 herbal extracts. Recommended respectively for men and women. Strengthen renal blood circulation, relieve colic.
Foreign urological dietary supplements are also sold in pharmacies:
- Urodan, Latvia. In a powder weighing 100 mg, 2.5 mg of piperazine, which alkalizes urine and converts calculi into soluble salts, bearberry extract 2.6 mg, urotropine 0.3 mg. Diuretic and disinfectant. Contraindicated in diabetes mellitus;
- Spilled, Indonesia. Tablets and capsules with extracts of kidney tea, sow thistle, papaya, cubeb pepper, philanthus, silkweed, imperanta. Removes small stones, while fighting infections and inflammation. Strengthens the effect of antibiotics, acts as a diuretic, slightly pain relief and relieves spasms.